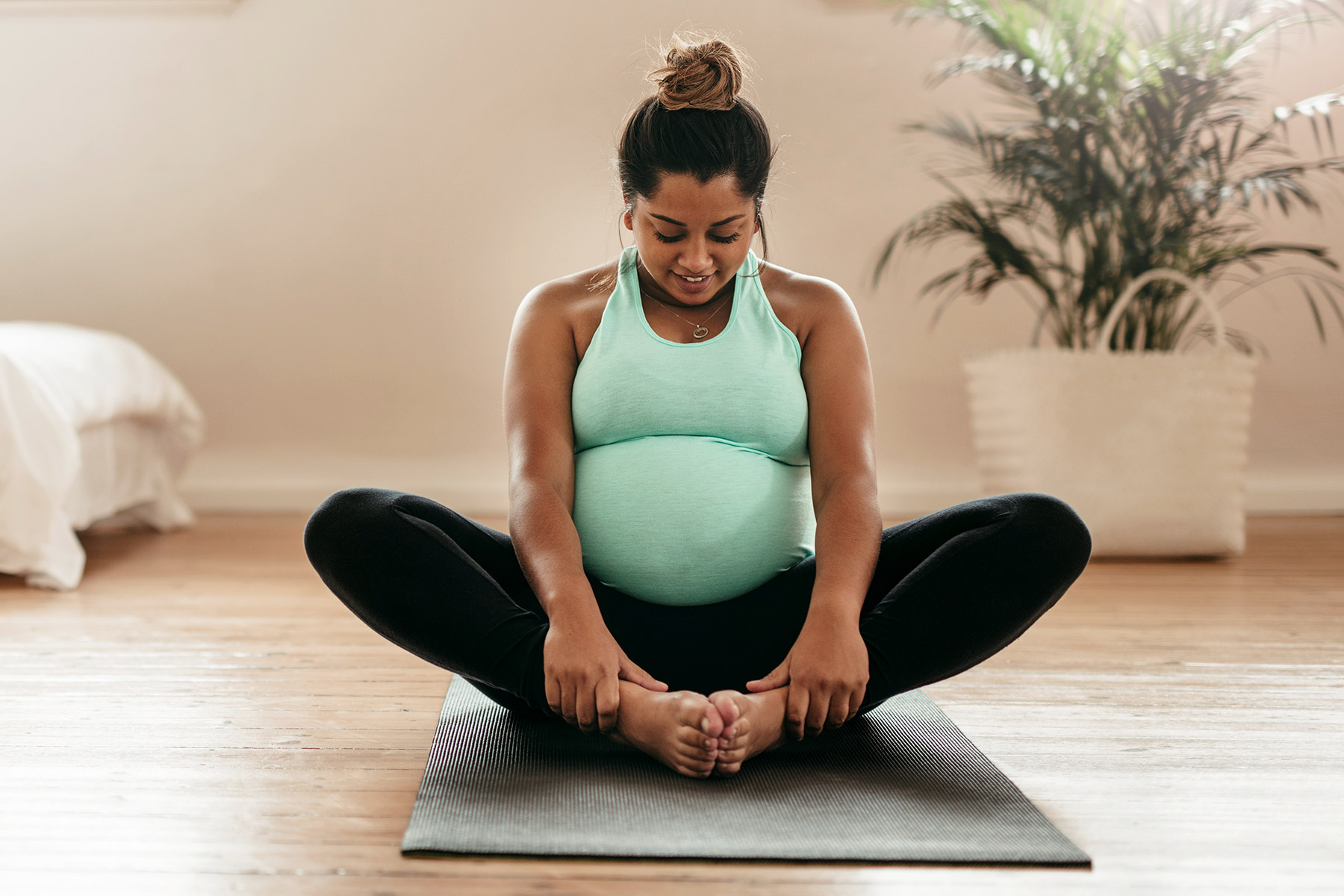
Pregnancy is a transformative journey that brings both joy and responsibility. Among the many aspects to consider is the importance of staying active. Exercise during pregnancy has numerous benefits for both the expectant mother and the developing baby.
However, it’s crucial to approach prenatal workouts with caution and awareness. This comprehensive guide explores safe workouts for expectant mothers, ensuring a healthy and active pregnancy.
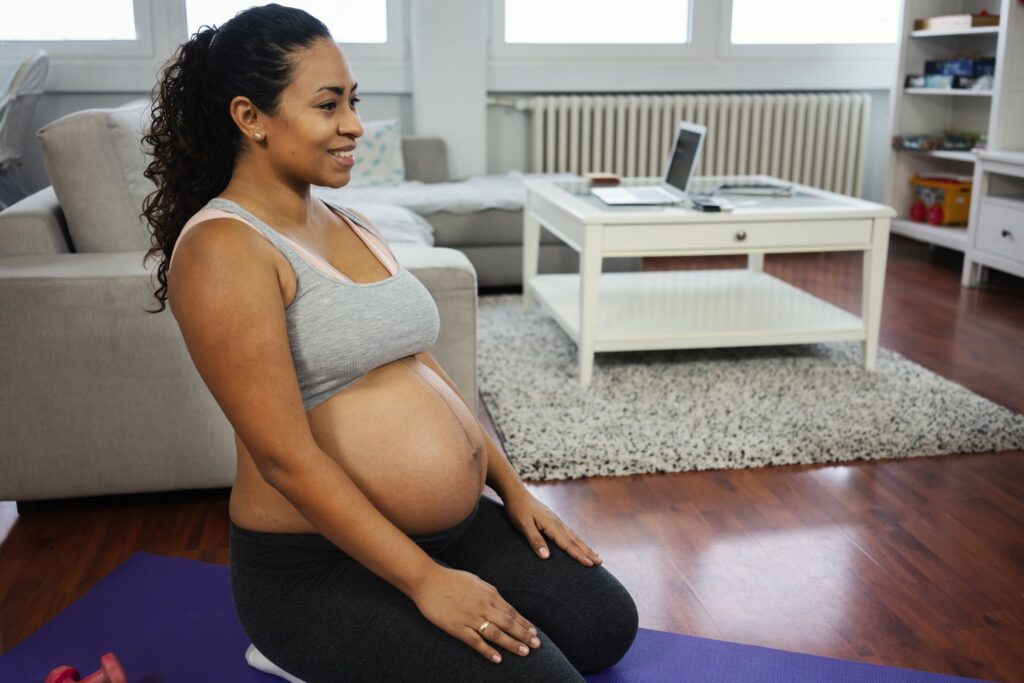

Benefits of Exercise During Pregnancy
Physical Benefits
Below are some of the benefits of exercise doing pregnancy:
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy heart and reduces the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension and gestational diabetes.
- Weight Management: Staying active helps manage pregnancy weight gain, making it easier to return to pre-pregnancy weight postpartum.
- Reduced Discomfort: Exercise can alleviate common pregnancy discomforts such as back pain, constipation, and swelling.
- Increased Stamina: Physical activity prepares the body for labor and delivery by increasing endurance and muscle strength.
Mental and Emotional Benefits
- Mood Enhancement: Exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Better Sleep: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, helping expectant mothers rest better.
- Stress Reduction: Engaging in regular exercise can help manage stress and anxiety levels during pregnancy.
General Guidelines for Exercise During Pregnancy
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting or continuing any exercise regimen during pregnancy, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and the specifics of your pregnancy.
Listen to Your Body
Pregnancy is a time to focus on gentle and moderate exercises rather than intense workouts. Pay attention to your body’s signals and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can be more risky during pregnancy. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your workouts to stay hydrated.
Avoid Overheating
Pregnant women are more prone to overheating. Exercise in a cool environment and avoid hot and humid conditions. Wear loose, breathable clothing to help regulate your body temperature.
Warm-Up and Cool Down
Always start with a warm-up to prepare your muscles and end with a cool down to gradually bring your heart rate back to normal. This can prevent injuries and reduce muscle soreness.
Safe Exercises for Expectant Mothers
Below are some exercises that expectant mother should follow:
1. Walking
Walking is one of the safest and most accessible exercises for pregnant women. It’s a low-impact activity that can be done anywhere and doesn’t require any special equipment.
- Benefits: Improves cardiovascular health, boosts mood, and helps with weight management.
- Tips: Aim for at least 30 minutes of brisk walking most days of the week. Wear supportive shoes and walk on flat, even surfaces.
2. Swimming
Swimming and water aerobics are excellent choices as the buoyancy of the water supports your weight, reducing stress on joints and ligaments.
- Benefits: Enhances cardiovascular fitness, improves muscle tone, and reduces swelling.
- Tips: Ensure the water temperature is comfortable, and avoid diving or jumping into the pool.
3. Prenatal Yoga
Prenatal yoga focuses on gentle stretching, breathing techniques, and relaxation, making it ideal for expectant mothers.
- Benefits: Increases flexibility, reduces stress, and improves posture and balance.
- Tips: Choose classes specifically designed for pregnant women and inform your instructor about your pregnancy.
4. Pilates
Pilates strengthens the core muscles, which can help support the extra weight of pregnancy and reduce back pain.
- Benefits: Improves posture, strengthens abdominal muscles, and enhances overall strength.
- Tips: Opt for prenatal Pilates classes and avoid exercises that involve lying on your back for extended periods.
5. Strength Training
Light strength training can help maintain muscle tone and strength, which is beneficial during pregnancy and labor.
- Benefits: Increases muscle endurance, supports joints, and enhances overall fitness.
- Tips: Use light weights and focus on controlled, slow movements. Avoid heavy lifting and exercises that strain the lower back.
6. Stationary Cycling
Stationary cycling is a safe, low-impact exercise that can be done indoors, providing a great cardiovascular workout.
- Benefits: Boosts cardiovascular health and improves leg strength.
- Tips: Adjust the bike to ensure a comfortable position and avoid high-intensity cycling.
Exercises to Avoid During Pregnancy
Below are some exercise to avoid during pregnancy:
1. High-Impact Activities
Activities such as running, jumping, and high-impact aerobics can put unnecessary stress on joints and the pelvic floor.
2. Contact Sports
Avoid sports that involve a high risk of falling or direct impact to the abdomen, such as soccer, basketball, and martial arts.
3. Hot Yoga and Hot Pilates
Exercising in hot environments can lead to overheating and dehydration, which can be harmful during pregnancy.
4. Activities with a Risk of Falling
Avoid activities with a high risk of falling, such as skiing, horseback riding, and outdoor cycling on uneven terrain.
Adjusting Exercise Routines by Trimester
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
- Focus on Building a Routine: Establish a regular exercise routine that includes low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga.
- Monitor Intensity: Keep workouts moderate in intensity, focusing on how your body feels.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-26)
- Maintain Activity Levels: Continue with your established routine but adjust as needed for comfort.
- Support Your Body: Use supportive gear, such as a belly band, to alleviate discomfort as your belly grows.
Third Trimester (Weeks 27-40)
- Prioritize Comfort: Choose exercises that are comfortable and avoid those that cause strain or discomfort.
- Focus on Flexibility and Relaxation: Incorporate more stretching and relaxation exercises to prepare for labor.
Signs to Stop Exercising and Seek Medical Advice
During pregnancy, it’s essential to be vigilant about your body’s signals. Stop exercising and consult your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Dizziness or Faintness: Feeling lightheaded can be a sign of dehydration or low blood pressure.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially when at rest, should be addressed immediately.
- Chest Pain: Any chest discomfort needs prompt medical attention.
- Calf Pain or Swelling: These could be signs of a blood clot and require immediate evaluation.
- Regular, Painful Contractions: These may indicate preterm labor.
- Decreased Fetal Movement: If you notice a significant reduction in your baby’s movements, seek medical advice.
Conclusion
Staying active during pregnancy is beneficial for both the expectant mother and the baby. With the right approach, exercise can help manage weight, reduce discomfort, and improve overall well-being.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen, listen to your body, and prioritize safety and comfort. By following these guidelines and choosing safe, appropriate workouts, you can enjoy a healthy and active pregnancy.